What is Inflammation?
Inflammation is a process by which your body's white blood cells and the things they make protect you from infection from outside invaders, such as bacteria and viruses. But in some diseases, like arthritis, your body's defense system -- your immune system -- triggers inflammation when there are no invaders to fight off. In these autoimmune diseases, your immune system acts as if regular tissues are infected or somehow unusual, causing damage.
Types Inflammation can be either short-lived (acute) or long-lasting (chronic). Acute inflammation goes away within hours or days. Chronic inflammation can last months or years, even after the first trigger is gone. Conditions linked to chronic inflammation include:
- Cancer
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- Asthma
- Alzheimer’s disease
Inflammation and Arthritis Some types of arthritis are the result of inflammation, such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Gouty arthritis
Other painful conditions of the joints and musculoskeletal system that may not be related to inflammation include osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, muscular low back pain, and muscular neck pain.
What Are the Symptoms of Inflammation?
Symptoms of inflammation include:
- Redness
- A swollen joint that may be warm to the touch
- Joint pain
- Joint stiffness
- A joint that doesn’t work as well as it should
Often, you’ll have only a few of these symptoms. Inflammation may also cause flu-like symptoms including:
- Fever
- Chills
- Fatigue/loss of energy
- Headaches
- Loss of appetite
- Muscle stiffness
What Causes Inflammation, and What Are Its Effects?
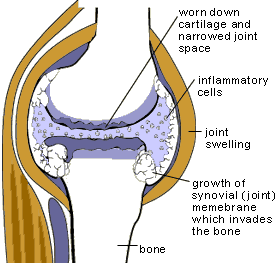
When inflammation happens, chemicals from your body's white blood cells enter your blood or tissues to protect your body from invaders. This raises the blood flow to the area of injury or infection. It can cause redness and warmth. Some of the chemicals cause fluid to leak into your tissues, resulting in swelling. This protective process may trigger nerves and cause pain.
Higher numbers of white blood cells and the things they make inside your joints cause irritation, swelling of the joint lining, and loss of cartilage (cushions at the end of bones) over time.
Home remedies
Some ways to ease long-term inflammation include:
- Quit smoking.
- Limit how much alcohol you drink.
- Keep a healthy weight.
- Manage stress.
- Get regular physical activity.
- Try supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, white willow bark, curcumin, green tea, or capsaicin. Magnesium and vitamins B6, C, D, and E also have some anti-inflammatory effects. Talk with your doctor before starting any supplement.
Anti-Inflammatory Diet
The things you eat and drink can also play a role in inflammation.
For an anti-inflammatory diet, include foods like:
- Tomatoes
- Olive oil
- Leafy green vegetables (spinach, collards)
- Nuts (almonds, walnuts)
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, sardines)
- Fruits (berries, oranges)
These things can trigger inflammation, so avoid them as much as you can:
- Refined carbohydrates (white bread)
- Fried foods (French fries)
- Sugary drinks (soda)
- Red and processed meats (beef, hot dogs)
- Margarine, shortening, and lard


Post a Comment